Background
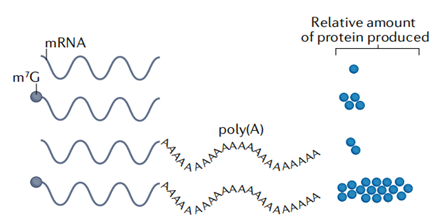
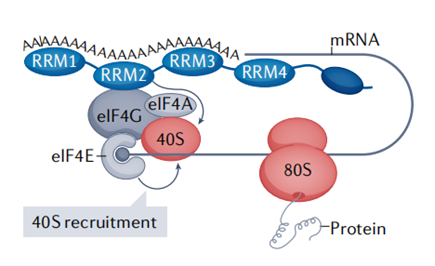
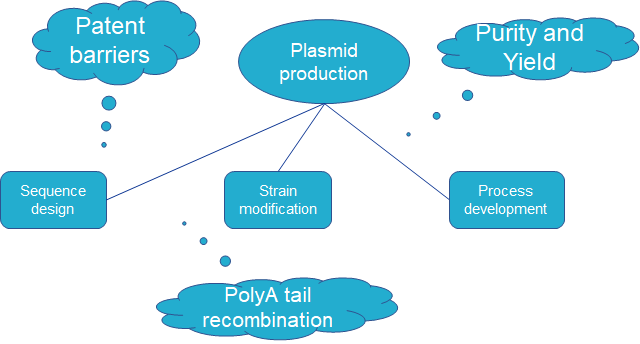
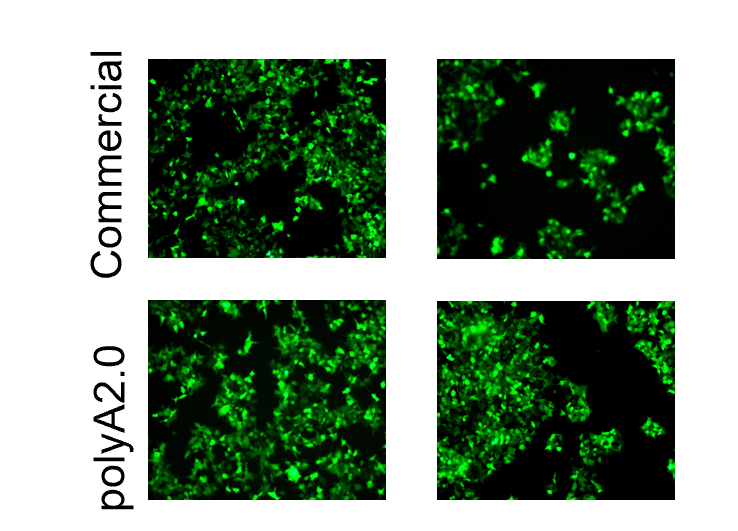
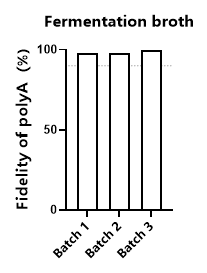
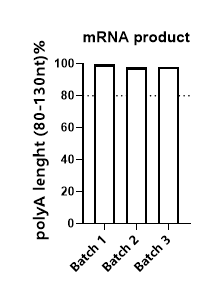
In eukaryotic organisms, poly A tail exists in almost every mRNA. The 3' end poly A tail plays a crucial role in the stability and translation of mRNA. It can prevent the degradation of 3’ end of mRNA by exonuclease. At the same time, it can bind PABPC, and then PABPC interact with eIF4G to form a "closed loop" structure, which helps to stimulate translation initiation. These functions are closely related to poly A tail, so the sequence design of poly A tail is one of the key factors for the quality assurance of mRNA products.