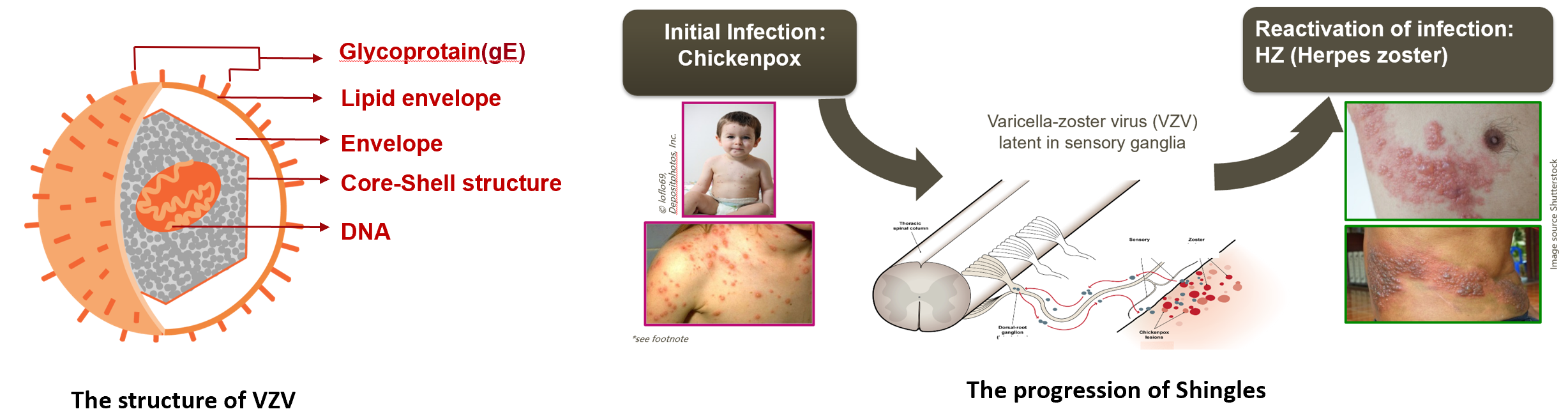
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an infectious disease caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which has been latent for a long time in the posterior root ganglia of the spinal cord or cranial ganglia . As the most important glycoprotein, gE is present in the cell membrane of the virion and plays an important role in adsorption and penetration of cells ,intercellular transmission.
Primary infection usually occurs in infants and children, with chickenpox as the main clinical manifestation. The virus enters the body through the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and spreads through the bloodstream, appearing as chickenpox on the skin. After invading the sensory nerve endings of the skin, it can move along the nerves to the ganglia of the posterior roots of the spinal cord and lurk in that place, presenting as an occult infection. When the body's immunity declines, the virus reactivates the infection and replicates in large quantities, and an immune response can occur in the peripheral sensory nerves and the unilateral dermatomes innervated by the nerves, causing herpes zoster, which is mainly characterized by erythema, blisters distributed in clusters, and neuralgia